Archive for the ‘Search’ Category.
22nd April 2013, 02:53 pm
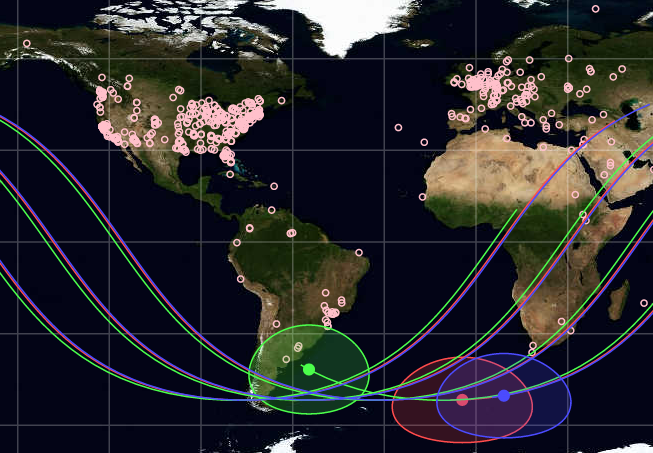 NASA has deployed three smartphone satellites (PhoneSats) into orbit. PhoneSat is a nanosatellite, categorizing the mass as between one and ten kilograms. Additionally, PhoneSat is a 1U CubeSat, with a volume of around one liter. The PhoneSat Project strives to decrease the cost of satellites while not sacrificing performance. In an effort to achieve this goal, the project is based around Commercial Off-The-Shelf electronics to provide functionality for as many parts as possible while still creating a reliable satellite.
NASA has deployed three smartphone satellites (PhoneSats) into orbit. PhoneSat is a nanosatellite, categorizing the mass as between one and ten kilograms. Additionally, PhoneSat is a 1U CubeSat, with a volume of around one liter. The PhoneSat Project strives to decrease the cost of satellites while not sacrificing performance. In an effort to achieve this goal, the project is based around Commercial Off-The-Shelf electronics to provide functionality for as many parts as possible while still creating a reliable satellite.
The satellites will send information about their health via radio back to Earth in an effort to demonstrate they can work as satellites in space. The spacecraft also will attempt to take pictures of Earth using their cameras.
PhoneSat satellites are emitting packets on the amateur radio spectrum to report different types of message. Amateur radio operators around the world can participate in the mission by monitoring transmissions and retrieving image data from the three satellites. Large images will be transmitted in small chunks and will be reconstructed through a distributed ground station network. More information can found on the on the PhoneSat website.
Category:
Search |
Comments Off on Smartphone Satellites
23rd March 2013, 12:06 pm
The Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) is a bureau of the United States Department of the Treasury which collects and analyzes information about financial transactions in order to combat domestic and international money laundering, terrorist financing, and other financial crimes. While addressing its actions against the Silk Road FinCEN’s director expressed its mission in November 2013 as “to safeguard the financial system from illicit use, combat money laundering and promote national security.”
On March 18th 2013, FinCEN published an interpretive guidance to clarify the applicability of the regulations implementing the Bank Secrecy Act (“BSA”) to persons creating, obtaining, distributing, exchanging, accepting, or transmitting virtual currencies. Such persons are referred to in this guidance as “users,” “administrators,” and “exchangers,” and are defined in the paper.
A user of virtual currency is not an MSB under FinCEN’s regulations and therefore is not subject to MSB registration, reporting, and recordkeeping regulations. However, an administrator or exchanger is an MSB under FinCEN’s regulations, specifically, a money transmitter, unless a limitation to or exemption from the definition applies to the person.
While FinCen created a new term – and by extension: a new law! – this ‘guidance’ might be used as pretense for future actions in the nascent cryptocurrency space.
More here
Category:
Search |
Comments Off on Creators of virtual currencies need a money transmitter license
7th December 2012, 06:01 pm
 Did you know that one Google search creates CO2 emissions of at least 1g? And Chris Goodall, author of Ten Technologies to Save the Planet, even estimates the carbon emissions of a Google search to even be more like 7g to 10g (assuming 15 minutes’ computer use). Wissner-Gross has also calculated the CO2 emissions caused by individual use of the internet. His research indicates that viewing a simple web page generates about 0.02g of CO2 per second. This rises tenfold to about 0.2g of CO2 a second when viewing a website with complex images, animations or videos. Nicholas Carr, author of The Big Switch, Rewiring the World, has calculated that maintaining an avatar in the Second Life virtual reality game, requires 1,752 kilowatt hours of electricity per year. That is almost as much used by the average Brazilian.
Did you know that one Google search creates CO2 emissions of at least 1g? And Chris Goodall, author of Ten Technologies to Save the Planet, even estimates the carbon emissions of a Google search to even be more like 7g to 10g (assuming 15 minutes’ computer use). Wissner-Gross has also calculated the CO2 emissions caused by individual use of the internet. His research indicates that viewing a simple web page generates about 0.02g of CO2 per second. This rises tenfold to about 0.2g of CO2 a second when viewing a website with complex images, animations or videos. Nicholas Carr, author of The Big Switch, Rewiring the World, has calculated that maintaining an avatar in the Second Life virtual reality game, requires 1,752 kilowatt hours of electricity per year. That is almost as much used by the average Brazilian.
But what’s much worse is that Google through its business model (AdWords/AdSense) has created a never-ending pollution engine for the World Wide Web. Since there’s is is money to be made by having a page show up in Google’s search results an entire industry sprung up our off nowhere (SEO). And every single ‘contributor’ to that industry has only one goal in mind: how can I get my page to show up on top of Google’s result to sell what I have to offer. To this day the Google algorithm still employs a largely popularistic approach: mainly a page’s importance is measured by how many other pages/sites point (link) to it. Every other aspect of the logic just provides nuances.
So, just like 85% of all emails sent are SPAM, it is very likely that 85% of pages on the World Wide Web are SPAM and a lot of it is being presented to you by Google (and of course any other search engine) as legitimate content. Just ask yourself: if you search for ‘best cell phone’, ‘best car loan’ – what do you expect to find? A legitimate research paper?
Category:
Search,
Technology |
Comments Off on How Google pollutes your environment
10th September 2012, 01:32 pm
 I guess Bob had it coming .. Yesterday domain hosted on GoDaddy’s DNS as well as GoDaddy hosted email accounts where taken down by a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack). In computing, a DoS attack or distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS attack; dns denial of service attack) is an attempt to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users. Although the means to carry out, motives for, and targets of a DoS attack may vary, it generally consists of the efforts of one or more people to temporarily or indefinitely interrupt or suspend services of a host connected to the Internet.
I guess Bob had it coming .. Yesterday domain hosted on GoDaddy’s DNS as well as GoDaddy hosted email accounts where taken down by a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack). In computing, a DoS attack or distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS attack; dns denial of service attack) is an attempt to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users. Although the means to carry out, motives for, and targets of a DoS attack may vary, it generally consists of the efforts of one or more people to temporarily or indefinitely interrupt or suspend services of a host connected to the Internet.
A member of Anonymous known as AnonymousOwn3r is claiming responsibility via Twitter, and makes it clear this is not an Anonymous collective action.
Category:
Search |
Comments Off on Anonymous takes down GoDaddy
22nd August 2012, 10:45 am
 Do you think of yourself as a Google user? Well, think again .. to Google you are the product! With pretty much all of Google’s revenues coming from its pay-per-click programs (AdWords/AdSense) Google is an advertising company selling you to its customers – the advertisers. Google’s model is to sell your attention – measured in clicks – on sponsored ads. The company manufactures more than one thousand of these actions per second. With the cost per click hovering around $1 Google made more than $1,000 in revenue per second which translates to more than $4.3 Million per day or close to $40 Billion for 2011 (see Google’s Income Statement). The more qualified the product (YOU) the more Google can charge to its clients. Fun Fact: The top pay-per-click term ‘auto-insurance-price-quotes’ generated almost $55 per click in 2011.
Do you think of yourself as a Google user? Well, think again .. to Google you are the product! With pretty much all of Google’s revenues coming from its pay-per-click programs (AdWords/AdSense) Google is an advertising company selling you to its customers – the advertisers. Google’s model is to sell your attention – measured in clicks – on sponsored ads. The company manufactures more than one thousand of these actions per second. With the cost per click hovering around $1 Google made more than $1,000 in revenue per second which translates to more than $4.3 Million per day or close to $40 Billion for 2011 (see Google’s Income Statement). The more qualified the product (YOU) the more Google can charge to its clients. Fun Fact: The top pay-per-click term ‘auto-insurance-price-quotes’ generated almost $55 per click in 2011.
In 2011, 96 % of Google’s revenue was derived from its advertising programs. For the 2006 fiscal year, the company reported $10.492 billion in total advertising revenues and only $112 million in licensing and other revenues. Google has implemented various innovations in the online advertising market that helped make it one of the biggest brokers in the market. Using technology from the company DoubleClick, Google can determine user interests and target advertisements so they are relevant to their context and the user that is viewing them. Google advertisements can be placed on third-party websites in a two-part program. Google’s AdWords allows advertisers to display their advertisements in the Google content network, through either a cost-per-click or cost-per-view scheme. The sister service, Google AdSense, allows website owners to display these advertisements on their website, and earn money every time ads are clicked.
Of course Google is not the only company that turns its users into products it just happens to be the most successful in doing so.
Category:
Search |
Comments Off on Google: YOU are the product
 NASA has deployed three smartphone satellites (PhoneSats) into orbit. PhoneSat is a nanosatellite, categorizing the mass as between one and ten kilograms. Additionally, PhoneSat is a 1U CubeSat, with a volume of around one liter. The PhoneSat Project strives to decrease the cost of satellites while not sacrificing performance. In an effort to achieve this goal, the project is based around Commercial Off-The-Shelf electronics to provide functionality for as many parts as possible while still creating a reliable satellite.
NASA has deployed three smartphone satellites (PhoneSats) into orbit. PhoneSat is a nanosatellite, categorizing the mass as between one and ten kilograms. Additionally, PhoneSat is a 1U CubeSat, with a volume of around one liter. The PhoneSat Project strives to decrease the cost of satellites while not sacrificing performance. In an effort to achieve this goal, the project is based around Commercial Off-The-Shelf electronics to provide functionality for as many parts as possible while still creating a reliable satellite.






